Understanding PMO meaning is essential for anyone involved in project management or organizational leadership. A Project Management Office (PMO) defines standards, oversees project execution, and ensures alignment with business goals. Knowing the role, functions, and responsibilities of a PMO helps improve efficiency, streamline processes, and drive successful project outcomes.
PMO Meaning in Modern Contexts

In today’s fast-paced digital world, the term PMO has multiple interpretations depending on the context. While traditionally known in business and project management, PMO has also become popular in texting, social media, and online slang.
Understanding these modern uses is crucial if you want to stay updated and communicate effectively online. Let’s explore the different contexts where PMO appears and what it really means.
PMO Meaning in Texting and Slang
In casual texting, PMO meaning can vary widely depending on the conversation. Many online users use PMO as a slang abbreviation, often to save time while chatting.
Understanding the intended meaning requires looking at the conversation context because PMO could refer to personal habits, online trends, or even humorous references. This modern usage is a reflection of how language evolves with digital communication.
PMO in Text Messages
When people type PMO in SMS or messaging apps, it’s often shorthand. Texting culture has embraced abbreviations to make communication faster, and PMO has emerged as one of those popular terms. It’s important to recognize the difference between professional and casual contexts.
For instance, a PMO in business refers to Project Management Office, while in text messages, it could imply a completely unrelated slang meaning.
PMO Meaning on TikTok

On platforms like TikTok, PMO meaning often trends in videos or challenges. Creators use the acronym as a catchy reference that resonates with viewers who understand the current slang.
TikTok’s fast-paced content encourages short forms and abbreviations, making PMO a part of modern social media lexicon. Knowing the TikTok-specific meaning ensures you don’t misinterpret content or hashtags.
PMO Meaning on Snapchat and Instagram
Snapchat and Instagram are visual-first platforms, yet PMO has made its way into captions, DMs, and hashtags. Users leverage PMO either to reference popular culture, online trends, or niche communities. Understanding PMO in these platforms helps you engage accurately with posts or conversations and avoid miscommunication.
PMO in Urban Dictionary
Urban Dictionary provides insights into how PMO meaning has evolved in digital culture. It lists user-submitted definitions that capture slang usage, trends, and informal contexts. Checking PMO on Urban Dictionary is useful if you want to stay updated on changing online language and its multiple interpretations across different communities.
Variations of PMO in Slang
Slang is rarely static, and PMO comes in various forms and interpretations. Depending on the platform, age group, or community, PMO could mean different things. Being aware of these variations is key to effective online communication. It also ensures that you are not caught off guard when encountering PMO in chats, captions, or forums.
PMO Meaning in Business

In the business world, PMO meaning refers to a Project Management Office, a critical organizational unit that ensures projects align with corporate goals, follow standard processes, and deliver consistent results. Understanding a PMO’s structure, functions, and benefits is essential for managers, team members, and stakeholders. Let’s dive into the details.
PMO Definition
A Project Management Office (PMO) is an organizational entity that centralizes project oversight, defines standards, and provides guidance for successful project delivery. Its primary aim is to ensure projects are executed efficiently, on time, and within budget. PMOs are key in maintaining project governance, risk management, and resource allocation.
PMO Objectives
The main objectives of a PMO include:
- Standardizing project management processes across the organization
- Improving project success rates
- Ensuring alignment with strategic business goals
- Facilitating resource allocation and optimization
- Monitoring project performance and KPIs
- Supporting risk and change management
- Enhancing communication across teams
PMO Types
PMOs can take several forms based on organizational needs:
- Supportive PMO – Provides templates, best practices, and guidance
- Controlling PMO – Enforces compliance with project standards
- Directive PMO – Directly manages and controls projects
- External PMO – Supports clients or external stakeholders
- Internal PMO – Focused on internal company projects
Core Functions of a PMO
The key functions of a PMO include:
- Project governance and oversight
- Resource and budget management
- Risk identification and mitigation
- Portfolio prioritization
- Process standardization
- Reporting and analytics
- Training and mentoring project managers
PMO Categories by Organizational Hierarchy
PMOs can be structured according to organizational hierarchy:
- Enterprise PMO (EPMO) – Oversees all projects across the organization
- Divisional PMO – Focuses on specific business units or departments
- Project-specific PMO – Created for major or strategic projects
PMO Examples in Real Organizations
Many successful companies implement PMOs to enhance project delivery. Examples include:
- IBM – Enterprise PMO for global projects
- Microsoft – Portfolio management office for software development
- Google – Departmental PMOs for product and innovation projects
PMO Software and Tools

Modern PMOs rely on specialized software for efficiency:
- Microsoft Project – Planning and scheduling
- Jira – Agile project tracking
- Asana & Trello – Task and workflow management
- Smartsheet – Portfolio tracking and analytics
- Monday.com – Team collaboration and reporting
PMO Certification and Membership
Certifications enhance PMO credibility and skills:
- PMP (Project Management Professional)
- PgMP (Program Management Professional)
- PMI-ACP (Agile Certified Practitioner)
- Certified Manager (CM)
- Membership in PMI (Project Management Institute) provides resources, training, and networking opportunities
PMO Challenges
PMOs face several challenges, including:
- Resistance to change from teams
- Difficulty enforcing standardized processes
- Limited executive support
- Balancing strategic and operational priorities
- Managing cross-functional resources
- Adapting to evolving business needs
PMO ROI and Benefits
A well-implemented PMO can deliver significant returns:
- Improved project success rates
- Reduced costs and resource waste
- Standardized processes for efficiency
- Clear project visibility for stakeholders
- Enhanced team collaboration
- Better decision-making through analytics
PMO vs Project Manager
While both are critical in project success, the difference lies in scope:
| Aspect | PMO | Project Manager |
| Scope | Oversees multiple projects, standardizes processes | Manages individual projects |
| Authority | Strategic guidance and governance | Operational execution |
| Focus | Portfolio success, resource allocation | Task completion and team management |
| Reporting | Reports to executives and stakeholders | Reports to PMO or senior management |
The Future of PMO
The future of PMOs is evolving with technology and business needs:
- Adoption of AI and automation for reporting and predictive analytics
- Agile and hybrid PMO models to support fast-changing projects
- Greater emphasis on strategic portfolio management
- Cloud-based collaboration tools to enable remote project teams
- Continuous improvement in PMO processes for efficiency and innovation
PMO Roles and Responsibilities
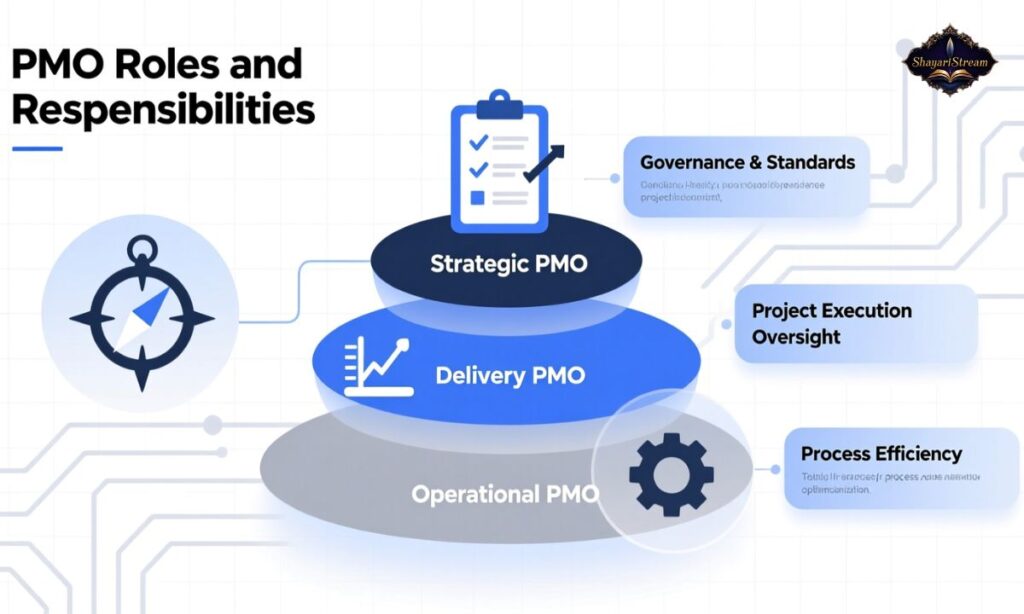
A Project Management Office (PMO) plays a critical role in ensuring that projects are delivered efficiently, strategically, and in alignment with organizational goals. Understanding the roles, responsibilities, and key positions within a PMO is essential for managers, team members, and organizations aiming for consistent project success. Let’s break down the various aspects of PMO roles and responsibilities.
PMO Roles and Responsibilities
The primary responsibilities of a PMO include:
- Project Governance: Establishing standards, policies, and procedures for all projects
- Resource Management: Allocating personnel, budgets, and tools efficiently
- Portfolio Oversight: Monitoring multiple projects to ensure alignment with strategic goals
- Risk and Issue Management: Identifying risks, mitigating issues, and ensuring continuity
- Performance Tracking: Measuring project success using KPIs and metrics
- Process Improvement: Implementing lessons learned and continuous improvement initiatives
- Stakeholder Communication: Ensuring transparency and updates for executives and teams
- Training and Mentorship: Supporting project managers and teams to enhance skills
What are Typical PMO Job Titles?
A PMO includes several key roles that ensure smooth operations:
- PMO Director: Oversees the entire PMO strategy and operations
- PMO Manager: Manages day-to-day activities and supports project managers
- PMO Analyst: Tracks metrics, generates reports, and evaluates project performance
- PMO Coordinator: Assists in planning, scheduling, and resource allocation
- PMO Process Specialist: Designs and enforces standardized project processes
Who Needs a Project Management Office?
Organizations that handle multiple projects or complex portfolios benefit from a PMO. Typical scenarios include:
- Large corporations managing diverse initiatives
- Companies undergoing digital transformation
- Organizations aiming to standardize project delivery
- Departments with cross-functional teams
- Businesses seeking improved ROI and strategic alignment
PMO Director and PMO Manager
The PMO Director sets the strategic direction, ensuring all projects align with organizational goals, while the PMO Manager oversees daily operations, resource management, and supports project managers. Together, they maintain project consistency, governance, and efficiency.
Project and Program Managers
Project and Program Managers are the operational backbone of a PMO:
- Project Managers handle individual projects, ensuring timelines, budgets, and quality standards are met
- Program Managers oversee related projects, ensuring they collectively meet business objectives
Both roles report to the PMO and rely on its guidance, standards, and tools to execute successfully
Support Roles
A PMO’s success depends on various support roles:
- Resource Coordinators – Manage staff allocation across projects
- Financial Analysts – Track budgets and financial performance
- Project Administrators – Handle documentation, scheduling, and logistics
- Quality Assurance Specialists – Ensure standards and compliance are met
PMO Trainers and Coaches
PMO Trainers and Coaches help teams and managers adopt project management best practices. Their responsibilities include:
- Conducting workshops on project methodologies
- Mentoring new project managers
- Providing guidance on tools, templates, and PMO processes
- Ensuring continuous learning and skills enhancement across the organization
How to Set Up and Manage a PMO
Setting up a Project Management Office (PMO) requires strategic planning, clear objectives, and the right tools. A well-structured PMO ensures that projects are aligned with organizational goals, completed on time, and delivered within budget. Whether you’re establishing your first PMO or upgrading an existing one, following best practices can make a significant difference in efficiency and outcomes.
How to Set Up a PMO in 2025
In 2025, PMOs are evolving with technology, remote teams, and agile methodologies. Key steps to set up a PMO include:
- Define the purpose and scope of the PMO clearly
- Align the PMO strategy with business goals and portfolio objectives
- Establish KPIs and success metrics for project performance
- Identify key stakeholders and secure executive support
- Choose the right team structure including managers, analysts, and coordinators
- Ensure compliance with industry standards and methodologies
- Plan for future scalability as the organization grows
Start with Clarity
Clarity is critical for a successful PMO:
- Clearly articulate the vision and mission of the PMO
- Communicate roles and responsibilities to all stakeholders
- Establish priorities and focus areas for projects
- Define success criteria for both projects and the PMO itself
- Ensure alignment with corporate strategy and objectives
Choose the Right PMO Model
Selecting the correct PMO model is essential to match organizational needs:
- Supportive PMO – Provides guidance, templates, and best practices
- Controlling PMO – Enforces processes, compliance, and standards
- Directive PMO – Directly manages projects and resources
- Hybrid PMO – Combines elements of the above for flexibility
- Evaluate your organization size, project complexity, and maturity level before deciding
Standardize Your Processes
Standardization ensures consistency and efficiency:
- Develop common project templates and documentation
- Implement standardized workflows for approvals, reporting, and monitoring
- Ensure risk and quality management protocols are consistent
- Provide training for staff to follow standardized processes
- Regularly review and update processes to adapt to organizational changes
Leverage AI Tools
AI and automation enhance PMO efficiency in 2025:
- Use AI-powered project planning tools for scheduling and forecasting
- Implement analytics dashboards to monitor performance in real-time
- Automate status reports, risk analysis, and resource allocation
- Use AI for predictive insights to prevent project delays
- Streamline communication using collaboration platforms integrated with AI
Ways to Control a Project Management Office
Controlling your PMO ensures projects stay on track:
- Enforce standard operating procedures and governance frameworks
- Regularly audit project performance and compliance
- Use dashboards and KPIs to track portfolio performance
- Conduct project reviews with key stakeholders
- Adjust processes and resources based on data-driven insights
How to Manage Your Project with a PMO Template
PMO templates streamline project management:
- Use templates for project charters, schedules, budgets, and risk registers
- Customize templates based on project size and complexity
- Track project progress using milestone-based templates
- Integrate templates with project management software
- Ensure templates are updated regularly for best practices
Types of PMOs
Understanding the different types of PMOs is essential for choosing the right structure that aligns with your organization’s goals. Each PMO type serves a distinct purpose, provides specific levels of control, and offers unique advantages. Let’s explore the main types of PMOs in detail.
Supportive PMO
A Supportive PMO provides guidance, templates, and best practices to project teams without enforcing strict control. It is ideal for organizations with low project management maturity. Key features include:
- Provides documentation, templates, and guidelines for project execution
- Offers coaching and mentoring for project managers
- Ensures knowledge sharing and lessons learned
- Facilitates communication and collaboration among teams
- Supports project consistency without enforcing compliance
Controlling PMO
A Controlling PMO enforces standardized processes and compliance across all projects. It balances guidance with authority to ensure projects follow defined methodologies. Key aspects:
- Implements project management standards and governance
- Monitors project compliance and risk management
- Conducts audits and regular reviews
- Provides tools and templates with mandatory usage
- Ensures projects align with organizational strategy
Directive PMO
A Directive PMO takes full control and management of projects within an organization. It is ideal for large or highly regulated enterprises. Key characteristics:
- Directly manages projects and resources
- Assigns project managers to initiatives
- Ensures strict adherence to timelines and budgets
- Provides centralized reporting and decision-making
- Drives strategic alignment across all projects
External PMO
An External PMO supports clients or external stakeholders rather than focusing solely on internal operations. It is common in consulting firms or outsourced project services. Key points include:
- Manages client projects and expectations
- Provides advisory and governance support
- Ensures deliverables meet client standards
- Offers scalable solutions for multiple clients
- Monitors project KPIs for external accountability
Internal PMO (Advantages & Disadvantages)
An Internal PMO operates within the organization to improve internal project management practices. Understanding its advantages and disadvantages helps determine its suitability:
Advantages:
- Centralizes project governance and oversight
- Improves resource allocation and efficiency
- Enhances communication and collaboration
- Supports organizational strategy and portfolio management
Disadvantages:
- May face resistance from project teams
- Requires significant investment in training and tools
- Can create bureaucracy if overly controlling
- Needs continuous alignment with changing business priorities
PMO and Career Growth

A career in a Project Management Office (PMO) offers diverse opportunities for growth, skill development, and strategic exposure. PMOs are central to project success, portfolio management, and organizational efficiency, making them a highly sought-after career path. Understanding the benefits, requirements, and certifications can help you advance effectively in this field.
Reasons to Consider Working in a PMO
Working in a PMO provides numerous advantages:
- Gain exposure to strategic projects across the organization
- Develop portfolio and program management skills
- Increase visibility among executives and key stakeholders
- Improve project processes and methodologies
- Opportunity to work with cross-functional teams
- Enhance leadership and decision-making skills
- Learn risk management and governance best practices
- Access to continuous learning and mentorship opportunities
Requirements for Working in a PMO
Entering a PMO career typically requires a combination of education, experience, and skills:
- Bachelor’s degree in business, IT, or management
- Experience in project coordination or management
- Strong communication and organizational skills
- Knowledge of project management methodologies (Agile, Waterfall, Hybrid)
- Analytical skills for monitoring KPIs and performance metrics
- Familiarity with project management software tools
- Optional: Master’s degree for senior-level positions
Certifications for PMO Job Roles
Certifications enhance credibility and open doors to advanced roles in a PMO:
- PMP (Project Management Professional) – Globally recognized for project managers
- PgMP (Program Management Professional) – For program-level oversight
- PMI-ACP (Agile Certified Practitioner) – For Agile-focused PMOs
- Certified Manager (CM) – General management and leadership skills
- ITIL4 Foundation Certification – For IT-related project environments
- PMI-RMP (Risk Management Professional) – Risk-focused expertise
Advance Your PMO Career with Online Courses
Online courses offer flexibility and access to top-tier PMO training:
- Coursera – PMP and advanced PMO courses
- edX – Project management and leadership certifications
- LinkedIn Learning – Practical PMO skills and software tools
- Udemy – Affordable courses for Agile, Scrum, and project planning
- Skillshare – Focused training on workflow optimization and collaboration
- Continuous learning through online courses ensures career progression and skill enhancement in a rapidly evolving PMO landscape
Quick References
To wrap up your understanding of PMO Meaning, it’s helpful to have a quick reference guide. This section provides a clear comparison, alternative meanings, and practical usage tips for PMO, ensuring you can apply this knowledge effectively in both business and casual contexts.
Quick Comparison Table – PMO Meanings
| Context | PMO Meaning | Key Points |
| Business / Corporate | Project Management Office | Oversees projects, ensures alignment with business goals, manages resources, tracks KPIs |
| Texting / Slang | Personal, playful, or online abbreviation | Used in casual chats; meaning depends on context |
| Social Media (TikTok / Instagram / Snapchat) | Trend-based abbreviation | Popular in hashtags and captions; reflects current slang trends |
| Urban Dictionary | User-submitted definitions | Shows evolving online usage and community-driven meanings |
This table helps differentiate PMO in professional vs casual contexts, which is crucial for accurate understanding.
What Else Can ‘PMO’ Mean?
Besides its widely known business definition, PMO can have other interpretations:
- Online slang or abbreviations in texting communities
- Specific references on social media platforms like TikTok or Instagram
- Cultural or humorous variations that emerge in forums or Urban Dictionary
- Understanding these alternative meanings ensures you communicate correctly in digital conversations and avoid misinterpretation
How to Use ‘PMO’ Correctly
Using PMO correctly depends on the context:
- In business: Always refer to Project Management Office, aligning with corporate strategy and project standards
- In casual messaging or social media: Check the context of the conversation or hashtags to infer the intended meaning
- Avoid mixing contexts: Using PMO in a professional email with slang meaning may create confusion
- Stay updated: Online meanings evolve, so refer to platforms like Urban Dictionary or trending social media references for current usage
Frequently Asked Questions
What does PMO mean in business?
PMO meaning in business refers to a Project Management Office, which oversees projects, standardizes processes, and ensures alignment with organizational goals.
What is the role of a PMO?
The role of a PMO is to manage project governance, allocate resources, monitor performance, and support project managers to deliver successful outcomes.
How does a PMO improve project success?
A PMO improves project success by providing standardized workflows, performance tracking, risk management, and strategic guidance for all projects.
What are the different types of PMOs?
The main types of PMOs include Supportive, Controlling, Directive, Internal, and External, each serving different levels of governance and control.
Who needs a Project Management Office?
Organizations with multiple projects or complex portfolios need a PMO to ensure efficiency, strategic alignment, and effective resource management.
How can I advance my career in a PMO?
Advancing in a PMO requires gaining experience, earning certifications like PMP or PgMP, developing project management skills, and leveraging online PMO courses.
Summary
Understanding PMO meaning helps professionals manage projects efficiently, align goals, and improve organizational success.
PMO guides project governance, standardizes processes, and offers career growth opportunities for aspiring project managers.

Sarah Mitchell is a creative writer and content enthusiast who believes in the timeless power of words. With a passion for literature and expression, she dedicates her work to crafting relatable and meaningful pieces that inspire and connect with readers.
At ShayariStream, Sarah focuses on curating English Shayari, Quotes, Messages, and Status & Meanings that capture emotions and moments in the most authentic way. Her writing reflects everyday feelings—from love and happiness to motivation and reflection—making it easy for people to find words that truly resonate.
Sarah’s mission is to help readers express their thoughts beautifully, whether it’s through a heartfelt message, an inspiring quote, or a simple status update. Her commitment to quality and creativity ensures that every visitor to ShayariStream leaves with words that add meaning to their lives.

